Heat pump
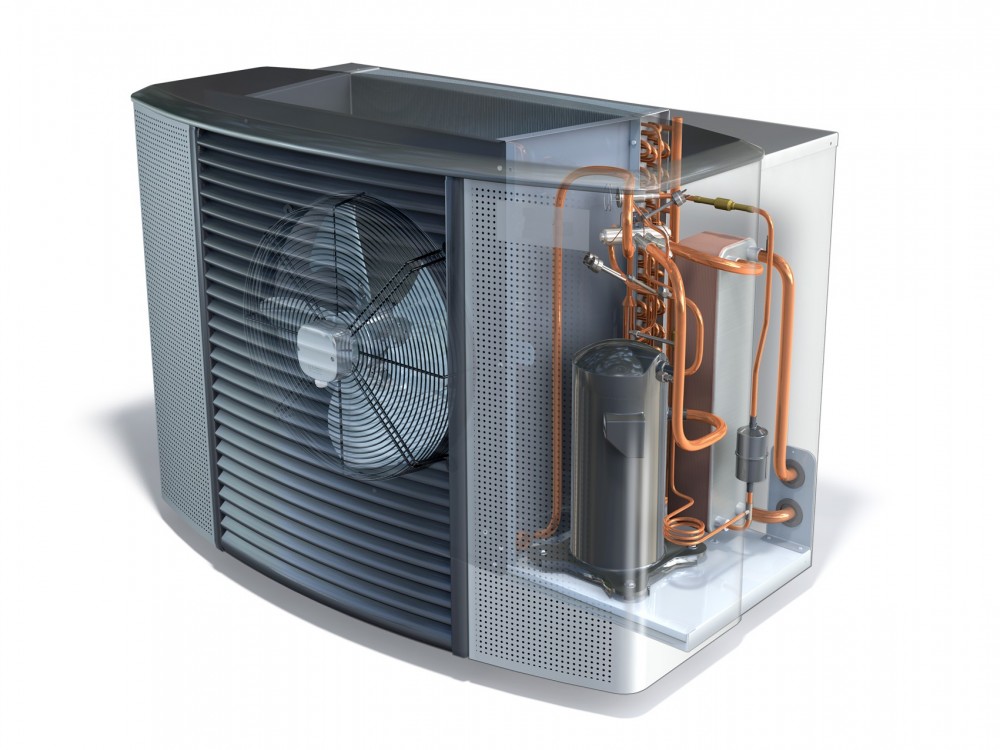
Heat pump is a complete heating and cooling system in which there is a reversible refrigeration cycle in order to the condenser to become the evaporator and vice versa.
Heat pump consists of:
• The compressor
• The condenser
• The evaporator
• The expansion valve
• The four-way valve
• The control system
The classification of the heat pump is based on:
1. The means where it pumps from and the means it expels: 
• Air-Air
• Air–Water
• Water-Air
• Ground-Air
• Ground-Water
2. The position of the various mechanisms :
• Uniform or autonomous (Compact)
• Split or bilateral type (Split Units)
3. The way the reversion is achieved :
• Fixed refrigerant circuit
• Variable refrigerant circuit
The categorization of heat pump applications is based on:
1. Low Temperature Cooling/ Heating up to 55oC
• Underfloor heating: The underfloor heating water temperature ranges from 35oC to 45oC
• Fan coil
• Cooling/ Cooling Ceiling/ Fan coil. In system cooling / cooling ceiling water temperature ranges from 7oC to 18oC. Control of the system is achieved by automating the control of dew point.
• Hot water (ΖΝΧ)
• Pool Heating
2. Middle temperatures up to 65oC
• The temperature ranges up to 65oC
• Installation on existing boiler system is simple and economical
3. High temperatures up to 80οC
• The temperature ranges up to 80οC
• Installation on existing boiler system is simple and economical
4. Geothermy
• Closed system of shallow geothermy.
• Open geothermy system
Benefits of Heat Pump
• Energy saving
• Enviromental Protection
• Installation - machinery space
• Maintenance cost
• Flexible interface applications
• Reliability - Quality
• Smart management





